Strings
Strings can be used to store text values. All string values can include Unicode values, emojis, tab characters, and line breaks.
CREATE person SET text = 'Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet';
Strings can be created using single quotation marks, or double quotation marks.
CREATE person SET text = "Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet";
Any string in SurrealDB can include Unicode text.
CREATE person SET text = "I ❤️ SurrealDB";
Strings can also include line breaks.
CREATE person SET text = "This
is
over
multiple
lines";
Specifying data type literal values using string prefixes
Overview
In SurrealQL, there are several data types for which literal values are specified using string values, with a prefix indicating the intended type for the value to be interpreted as.
Previously, in SurrealQL version 1.0, literal values of these types were simply specified using a string without any prefix, and SurrealDB would eagerly convert the strings into the relevant data type in any case where the string matched the format expected for that type. However, since SurrealQL version 2.0, strings are no longer eagerly converted into other data types. Instead, if you want to specify a literal value of one of these data types, you must explicitly use a string with the appropriate prefix.
Record ID literal values using the r prefix
The r prefix tells the parser that the contents of the string represent a record ID. The parser expects record IDs to have the following format: table_name:record ID.
All strings since SurrealDB 2.0 without the r prefix are of type string and are not parsed as records unless the prefix is present.
Here is an example of a record ID literal value, specified using a string with the r prefix.
RETURN r"person:john";
Response
In the example below, using the type::is_string() and type::is_record() functions respectively, you can check the type of the string.
RETURN type::is_string("person:john");
RETURN type::is_record("person:john");
RETURN type::is_record(r"person:john");
Response
Datetime literal values using the d prefix
The d prefix tells the parser that the contents of the string represent a datetime. The parser expects datetime values to have a valid RFC 3339 format. Here are a few examples:
RETURN d"2025-11-28T11:41:20.262Z";
RETURN d"2025-11-28T11:41:20.262+04:00";
RETURN d"2025-11-28T11:41:20.262-04:00";
RETURN d"2025-11-28T11:41:20Z";
RETURN d"2025-11-28T11:41:20+04:00";
Response
d'2025-11-28T11:41:20.262Z'
d'2025-11-28T07:41:20.262Z'
d'2025-11-28T15:41:20.262Z'
d'2025-11-28T11:41:20Z'
d'2025-11-28T07:41:20Z'
UUID literal values with the u prefix
The u prefix tells the parser that the contents of the string represent a uuid. The parser expects uuid values to follow the format of an UUID, ffffffff-ffff-ffff-ffff-ffffffffffff, where each non-hyphen character can be a digit (0-9) or a letter between a and f (representing a single hexadecimal digit).
RETURN u"8c54161f-d4fe-4a74-9409-ed1e137040c1";
Response
u'8c54161f-d4fe-4a74-9409-ed1e137040c1'
Byte values using the b prefix
b"0099aaff"
File paths using the f prefix
f"bucket:/some/key/to/a/file.txt";
f"bucket:/some/key/with\ escaped";
f"bucket:/some/key".put(b"00aa");
f"bucket:/some/key".get();
String prefixes vs. casting
String prefixes seem outwardly similar to casting, but differ in behaviour. A string prefix is an instruction to the parser to treat an input in a certain way, whereas a cast is an instruction to the database to convert one type into another.
As a result, incorrect input with a cast will generate an error:
RETURN <uuid>"018f0e6a_9b95-7ecc-8a38-aea7bf3627dd";
RETURN <datetime>"2024_06-06T12:00:00Z";
Response
"Expected a uuid but cannot convert '018f0e6a-9b95-7ecc-8a38-aea7bf3627d' into a uuid"
"Expected a datetime but cannot convert '2024-06-06T12:00:00' into a datetime"
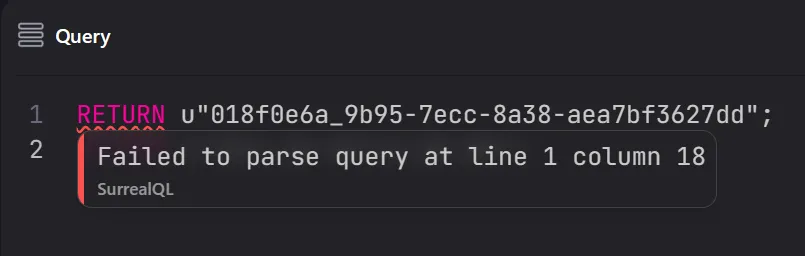
But the same input using a string prefix will not even parse until the input is valid.
RETURN u"018f0e6a_9b95-7ecc-8a38-aea7bf3627dd";
RETURN d"2024_06-06T12:00:00Z";
This also allows for immediate error messages on which part of the input is incorrect. As seen in the image below, the parser is able to inform the user that an underscore at column 18 is the issue.