In this section, you will explore writing GraphQL queries in Surrealist. The GraphQL query view in Surrealist provides a rich set of features, including syntax highlighting, query validation, and query execution. You can see the results of your queries in JSON structure returned by GraphQL.
Before you can start making queries, you need to start SurrealDB with the GraphQL module enabled. You can do this by starting a new instance of SurrealDB with the surreal start command.
surreal start --log debug --user root --password secret
surreal start --log debug --user root --password secret
After starting the SurrealDB instance, you can navigate to the Surrealist to start a new connection.
In the top left corner of the Surrealist, start a new connection. Ensure that the connection information is the same as the one you used to start the SurrealDB instance. In the example above we have set the user to root and the password to secret.
ImportantQuerying via GraphQL is not supported in the Surrealist sandbox.
Learn more about starting a connection in the Surrealist documentation.
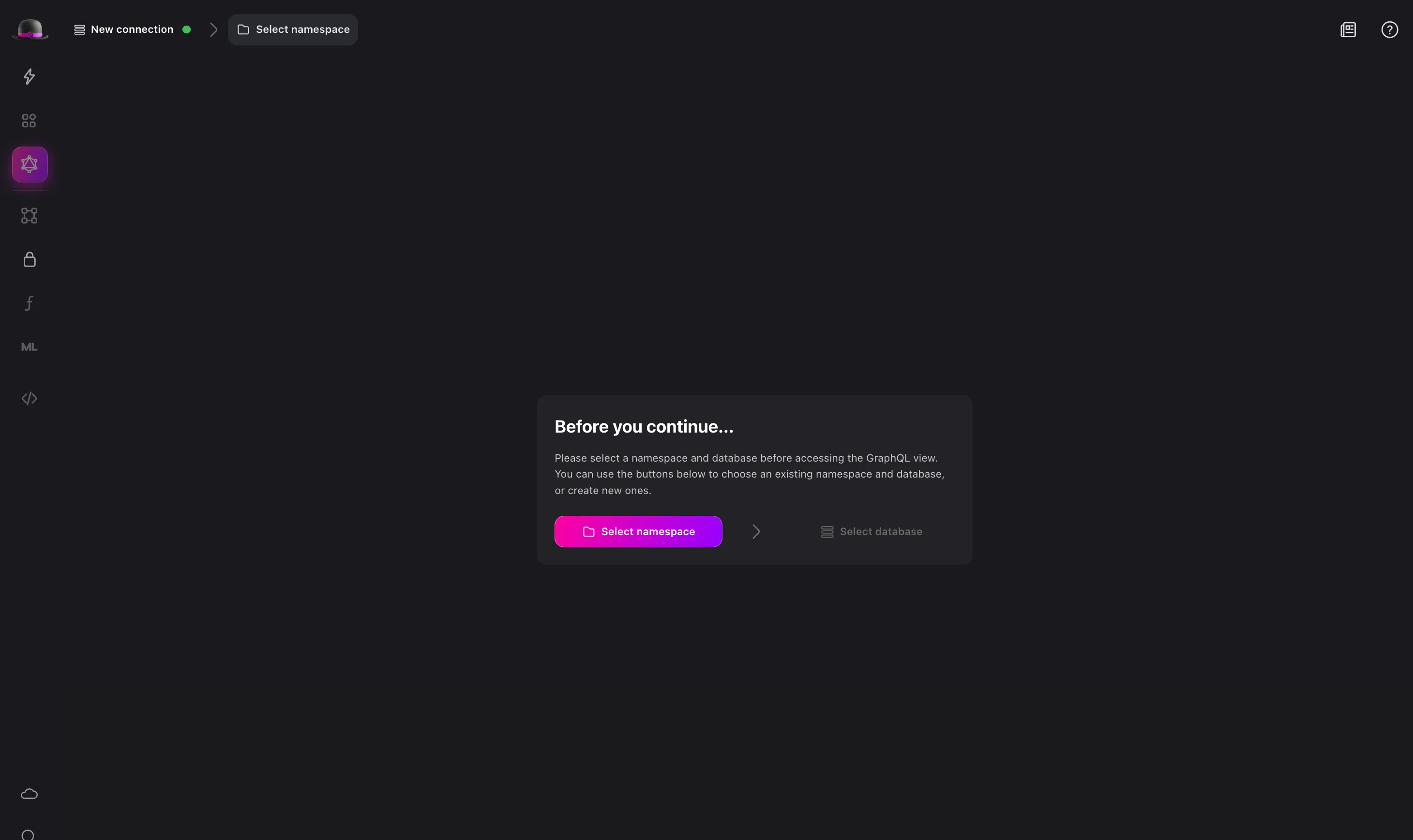
Before you can start writing queries, you need to set the namespace and database you want to use. For example, you can set the namespace to test and the database to test. This will set the namespace and database for the current connection.
Additionally, you can start a serving in Surrealist which also enables GraphQL automatically, starting a server on http://localhost:8000 by default for a root user with username and password root.
Next, use the SurrealQL query editor to create some data. For example, you can create a new user table with fields for firstName, lastName, and email and add a new user to the database.
In order to allow querying the created table using GraphQL, you will need to explicitly enable GraphQL using the DEFINE CONFIG statement. This will allow you to query the table using GraphQL on a per-database basis.
This must be followed by statements to explicitly define the resources to query. That is, you must use the DEFINE TABLE statement to define the table, and DEFINE FIELD statement to define the fields for the table. This is because GraphQL differs from SurrealDB itself in requiring resources to be defined before they can be used.
After you have created some data, you can start writing GraphQL queries. You can use the Surrealist GraphQL editor to write your GraphQL queries.
For example, to query the person table for all records, you can write the following GraphQL query:
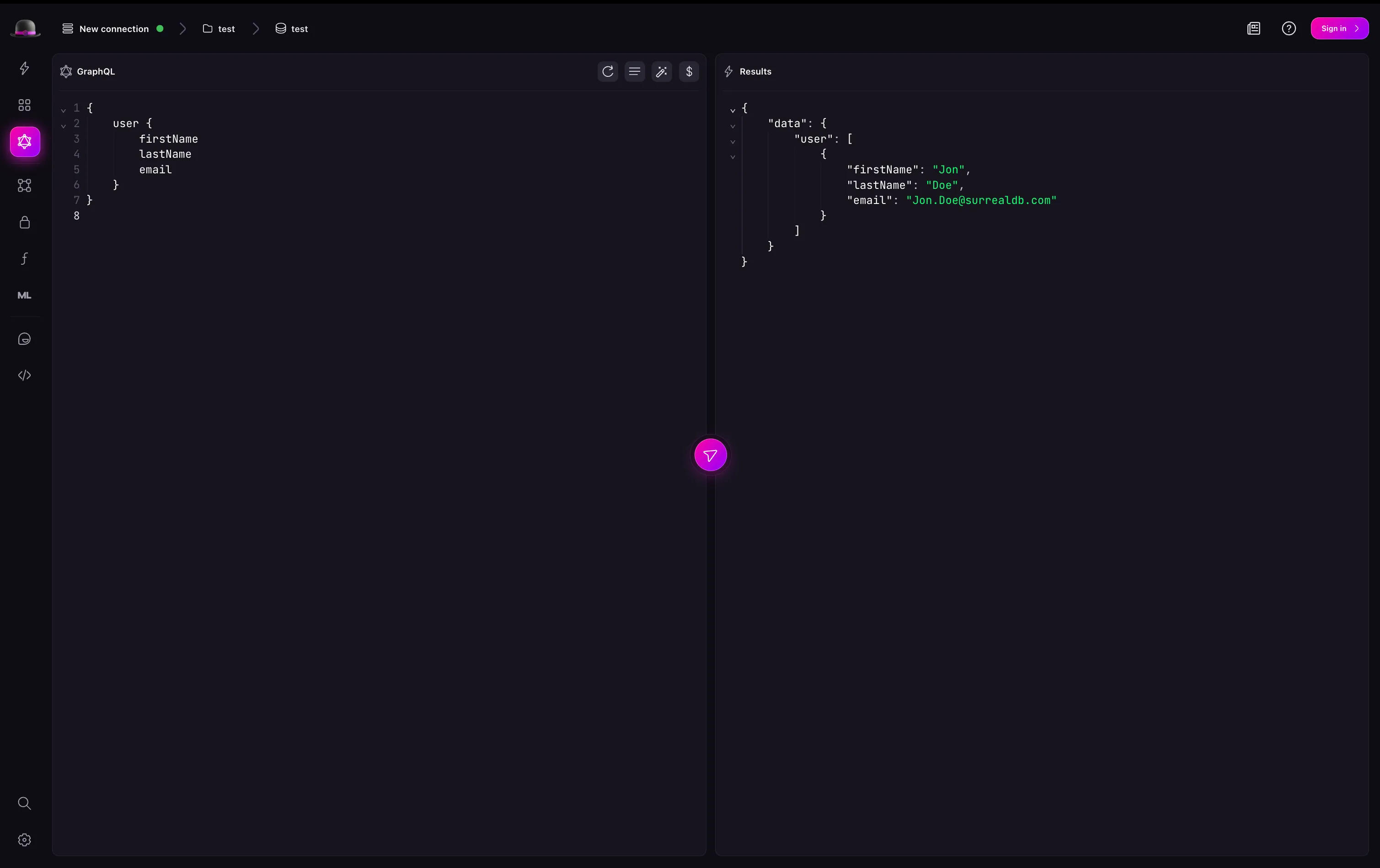
And to get the person with the email “Jon.Doe@surrealdb.com”, you can write the following GraphQL query:
Surrealist will automatically validate the query and provide you with the results.
Surrealist also supports introspection with GraphQL. This means that you can query the database and Surrealist will automatically infer the type of the data you are querying. For example, if you query the user table for all records, Surrealist will automatically infer the type of the data to be user.
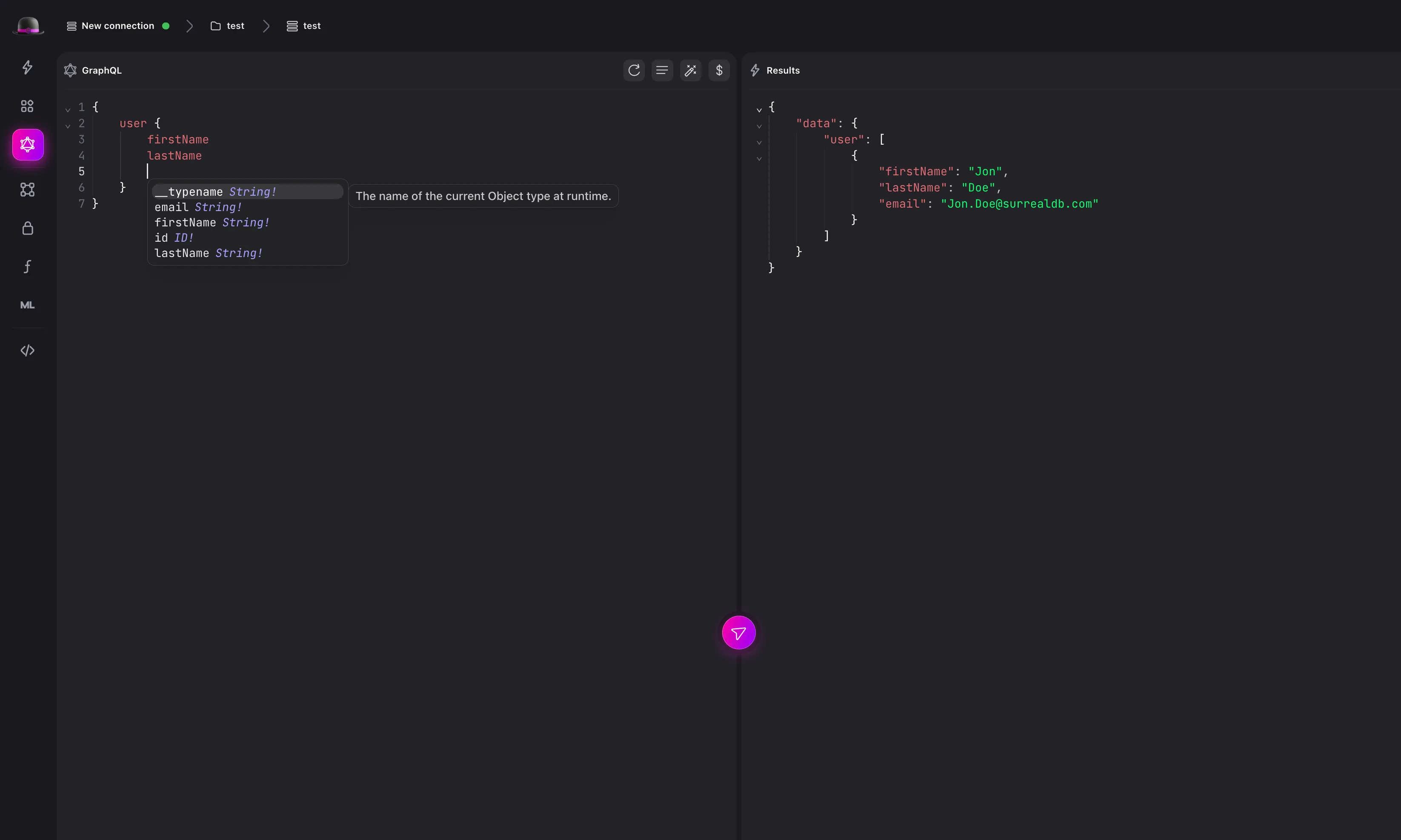
To learn more about the GraphQL view in Surrealist, check out the Surrealist documentation.