Upgrading from 2.x to 3.x
This guide consolidates all breaking changes when upgrading from SurrealDB 2.x to 3.x, organised by severity level. If you are using Surrealist, you can use the migration diagnostics to automatically see your data. This will also provide you with a list of actions you need to take to migrate your data.
Migration diagnostics in Surrealist
Surrealist provides a built-in migration diagnostics tool that can be used to automatically see your data and provide you with a list of actions you need to take to migrate your data.
The migration diagnostics tool is only available for SurrealDB version 2.6.1 and above.
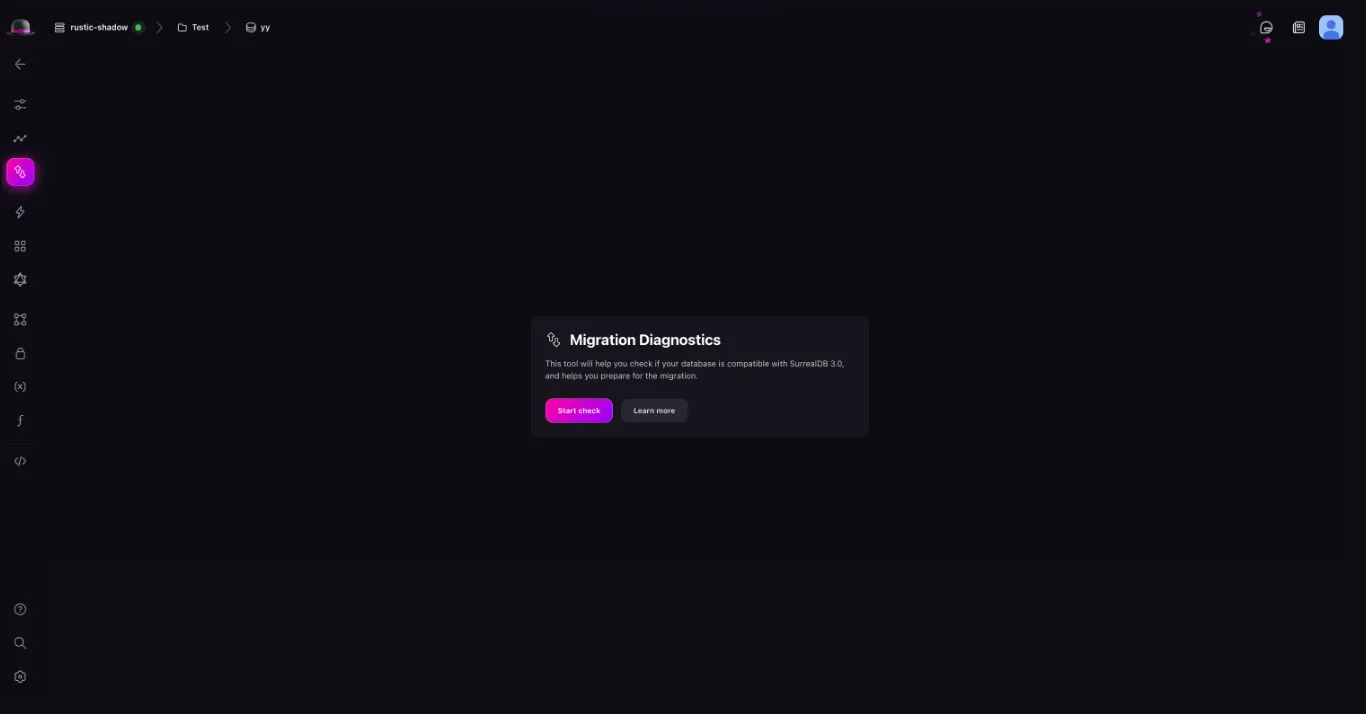
Select your 2.x database and click on the Migration option in the sidebar. This will open the migration diagnostics tool. First you’ll need to start the checks by clicking on the Start Checks button. This will return a migration report with a list of actions you need to take to migrate your data (If any).

After resolving the issue, click on the Mark as resolved button to mark the issue as resolved. This will remove the issue from the migration report.
Once all issues have been resolved, the migration diagnostics tool will allow you to export a V3 Compatible Export that can be imported into your updated SurrealDB 3.x instance.
V3 compatible export
Starting with SurrealDB 2.6.0, you can export your database in a format that is compatible with version 3.x. This export automatically performs several transformations to ensure your data and schema work correctly in version 3.x.
The V3 Compatible Export automatically handles the following transformations:
- Function name updates: All deprecated function names are automatically renamed to their new versions.
duration::from::* → duration::from_*string::is::* → string::is_*type::is::* → type::is_*time::is::* → time::is_*time::from::* → time::from_*rand::guid() → rand::id()type::thing → type::record
See the complete function mapping table below for the full list of function name updates.
SEARCH ANALYZER → FULLTEXT ANALYZER: Index definitions using SEARCH ANALYZER are automatically converted to FULLTEXT ANALYZER.- Parameter declarations: Automatically adds
LET keyword where required for parameter declarations MTREE → HNSW conversion: Vector search indexes using the deprecated MTREE type are automatically converted to use HNSW.- Future to COMPUTED field conversion: Where possible,
<future> fields are automatically converted to COMPUTED fields.
What requires manual migration
Some changes cannot be automatically converted and require manual intervention:
- Futures stored in records (using
DEFAULT <future> or CREATE ... SET field = <future>) - Nested fields with
<future> values - Queries using both GROUP and SPLIT clauses
- Code using removed operators (
~, !~, ?~, *~) - Stored closures in records
- Record reference syntax
ANALYZE statement usage
Using V3 compatible export
After completing the migration diagnostics in Surrealist and resolving all flagged issues, you can export your database using the v3 compatible export feature. This will generate a .surql file that can be safely imported into SurrealDB 3.x.
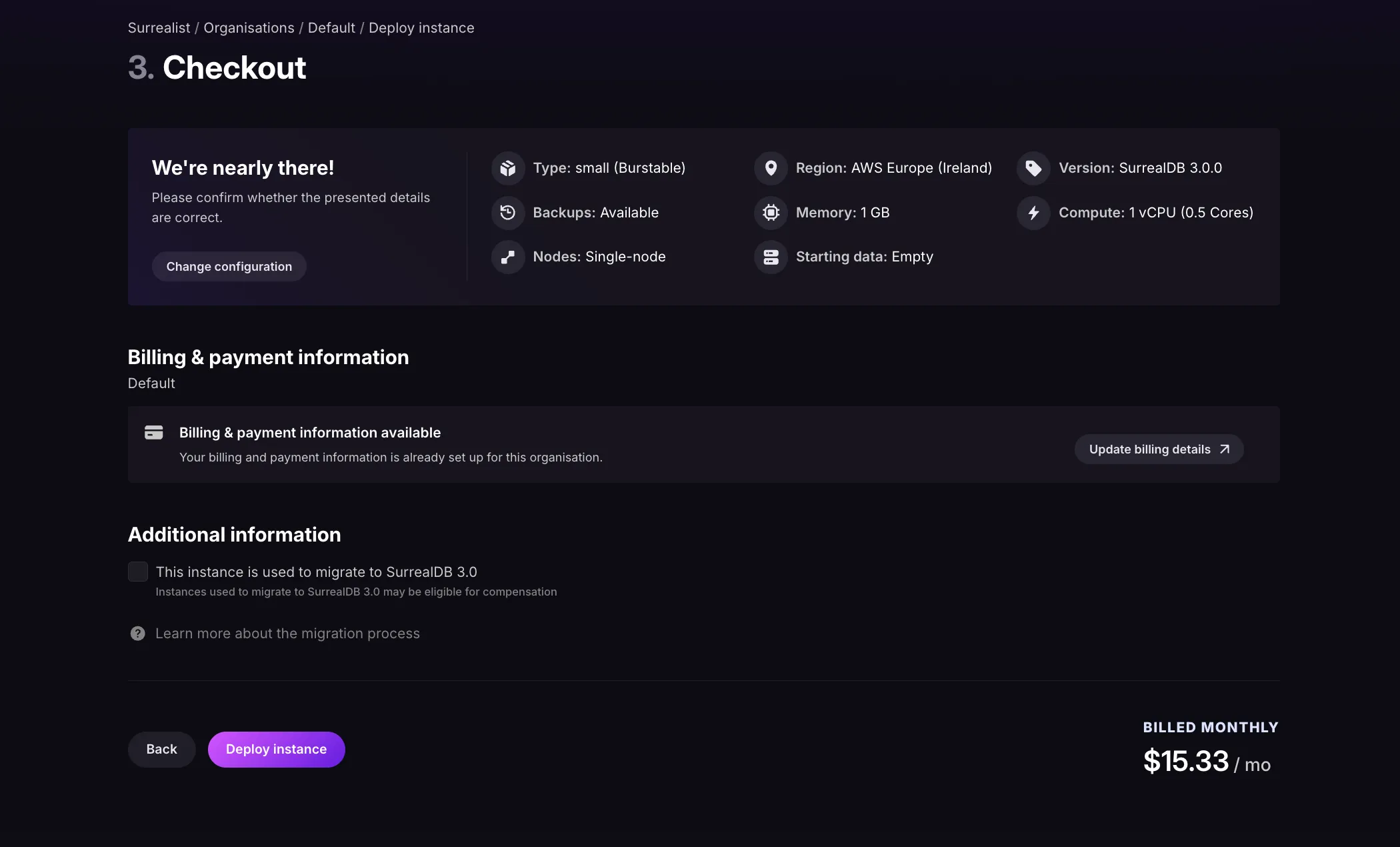
Next, in the Surrealist overview page, click on Deploy instance select the available plan and configure your instance (you can opt to upload a file to this instance with the v3 compatible export file).
At checkout, you will be prompted to enter your payment details (if you don’t have a payment method on file) and indicate that the instance is used to migrate to SurrealDB 3.0. This will let us know to give you migration credits on your account.
Severity Levels
In this section, we will explore the different severity levels of the migration report and the actions you need to take to migrate your data. These severity levels are as follows:
- Will break: Almost guaranteed to change query semantics when porting to
3.x. - Can break: Some use cases will remain the same, but likely to cause issues.
- Unlikely break: Only affects edge cases or rare usage patterns.
Will break - critical changes
1. Futures replaced with COMPUTED Fields
Severity: Will break
What changed: The <future> type has been completely removed and replaced with COMPUTED fields.
Migration actions:
- Use the migration tool to automatically convert futures where possible.
- Manually replace
VALUE <future> { expression } with COMPUTED expression. - Restructure code for cases where automatic conversion isn’t possible (nested fields,
DEFAULT futures).
Before (2.x):
DEFINE FIELD age ON person VALUE <future> { time::year(time::now()) - time::year(born) };
CREATE foo SET field = <future> { expression };
After (3.x):
DEFINE FIELD age ON person COMPUTED time::year(time::now()) - time::year(born);
For futures stored in records (using DEFAULT <future> or CREATE ... SET field = <future>), there is no direct replacement in 3.x. Fixing these cases will require re-architecting your schema, as storing arbitrary queries in record data is no longer supported.
COMPUTED restrictions:
- Can only be used in
DEFINE FIELD statements - No nested fields allowed inside or under
COMPUTED fields - Cannot be used on ID fields
- Cannot combine with:
VALUE, DEFAULT, READONLY, ASSERT, REFERENCE, FLEXIBLE - Only works on top-level fields, not nested fields
Example - nested field workaround:
DEFINE FIELD name.full ON person VALUE <future> { name.first + ' ' + name.last };
DEFINE FIELD full_name ON person COMPUTED name.first + ' ' + name.last;
2. Function name changes
Severity: Will break
Action: Update all function names according to the mapping table below.
Reason for Changes:
::is:: and ::from:: → ::is_ and ::from_ (matches method syntax)thing → record (consistent terminology)rand::guid() → rand::id() (default record ID format)string::distance::osa_distance → string::distance::osa (remove redundancy)
Complete mapping table:
| New Function Name | Previous name |
|---|
duration::from_days | duration::from::days |
duration::from_hours | duration::from::hours |
duration::from_micros | duration::from::micros |
duration::from_millis | duration::from::millis |
duration::from_mins | duration::from::mins |
duration::from_nanos | duration::from::nanos |
duration::from_secs | duration::from::secs |
duration::from_weeks | duration::from::weeks |
geo::is_valid | geo::is::valid |
string::distance::osa | string::distance::osa_distance |
string::is_alphanum | string::is::alphanum |
string::is_alpha | string::is::alpha |
string::is_ascii | string::is::ascii |
string::is_datetime | string::is::datetime |
string::is_domain | string::is::domain |
string::is_email | string::is::email |
string::is_hexadecimal | string::is::hexadecimal |
string::is_ip | string::is::ip |
string::is_ipv4 | string::is::ipv4 |
string::is_ipv6 | string::is::ipv6 |
string::is_latitude | string::is::latitude |
string::is_longitude | string::is::longitude |
string::is_numeric | string::is::numeric |
string::is_record | string::is::record |
string::is_semver | string::is::semver |
string::is_url | string::is::url |
string::is_ulid | string::is::ulid |
string::is_uuid | string::is::uuid |
time::is_leap_year | time::is::leap_year |
time::from_nanos | time::from::nanos |
time::from_micros | time::from::micros |
time::from_millis | time::from::millis |
time::from_secs | time::from::secs |
time::from_ulid | time::from::ulid |
time::from_unix | time::from::unix |
time::from_uuid | time::from::uuid |
type::is_array | type::is::array |
type::is_bool | type::is::bool |
type::is_bytes | type::is::bytes |
type::is_collection | type::is::collection |
type::is_datetime | type::is::datetime |
type::is_decimal | type::is::decimal |
type::is_duration | type::is::duration |
type::is_float | type::is::float |
type::is_geometry | type::is::geometry |
type::is_int | type::is::int |
type::is_line | type::is::line |
type::is_none | type::is::none |
type::is_null | type::is::null |
type::is_multiline | type::is::multiline |
type::is_multipoint | type::is::multipoint |
type::is_multipolygon | type::is::multipolygon |
type::is_number | type::is::number |
type::is_object | type::is::object |
type::is_point | type::is::point |
type::is_polygon | type::is::polygon |
type::is_range | type::is::range |
type::is_record | type::is::record |
type::is_string | type::is::string |
type::is_uuid | type::is::uuid |
type::record | type::thing |
Learn more about the database functions in the SurrealQL functions documentation.
3. array::range argument changes
Severity: Will break
What changed: Arguments changed from (offset, count) to (start, end) or accepting a range.
Action: Change all array::range calls to use start/end bounds instead of offset/count.
Before (2.x):
array::range(0, 5)
array::range(-1, 5)
array::range(-5, 5)
After (3.x):
array::range(0, 5)
array::range(-1, 5)
array::range(-5, 5)
array::range(0..=1)
Migration formula:
- Old:
array::range(offset, count) - New:
array::range(offset, offset + count)
4. LET required for parameters
Severity: Will break
What changed: Parameter declarations now require LET keyword.
Action: Add LET before all parameter declarations.
Before (2.x):
$val = 10;
After (3.x):
LET $val = 10;
Error Message:
Parse error: Parameter declarations without `let` are deprecated.
Replace with `let $val = ...` to keep the previous behavior.
5. GROUP and SPLIT cannot be used together
Severity: Will break
What changed: Using both GROUP and SPLIT in the same query is no longer allowed.
Action: Remove SPLIT from any query which also had a GROUP clause, as its inclusion had no effect in 2.x. If the use of both a SPLIT and a GROUP is required, put one of the two clauses into a subquery.
Before (2.x):
SELECT age, emails FROM user SPLIT emails GROUP BY age;
After (3.x) - Option 1 (split then group):
SELECT age, emails FROM (SELECT * FROM user SPLIT emails) GROUP BY age;
After (3.x) - Option 2 (group then split):
SELECT * FROM (SELECT age, emails FROM user GROUP BY age, emails) SPLIT emails;
6. Like operators removed
Severity: Will break
What changed: The ~, !~, ?~, *~ operators have been removed.
Action: Replace with string::distance or string::similarity functions.
Reason: Multiple similarity algorithms now available; users should choose their own cutoff point.
Before (2.x):
"Mario" ~ "mario";
After (3.x):
string::similarity::jaro("Mario", "mario") > 0.8;
DEFINE FUNCTION fn::similar($one: string, $two: string) -> bool {
string::similarity::jaro($one, $two) > 0.8
};
fn::similar("Mario", "mario");
Available Functions:
string::similarity::jaro()string::distance::osa()- And other similarity/distance functions
7. SEARCH ANALYZER → FULLTEXT ANALYZER
Severity: Will break
Action: Replace all instances of SEARCH ANALYZER with FULLTEXT ANALYZER.
Before (2.x):
DEFINE INDEX userNameIndex ON TABLE user
COLUMNS name SEARCH ANALYZER example_ascii BM25 HIGHLIGHTS;
After (3.x):
DEFINE INDEX userNameIndex ON TABLE user
COLUMNS name FULLTEXT ANALYZER example_ascii BM25 HIGHLIGHTS;
8. Database-Level strictness
Severity: Will break (if using --strict flag)
What changed: Strictness moved from instance-level flag to database-level definition.
Action: Add STRICT to DEFINE DATABASE statements for databases that need strictness.
Before (2.x):
surreal start --strict
After (3.x):
DEFINE DATABASE mydb STRICT;
Impact: Allows different databases on the same instance to have different strictness levels.
9. MTREE removal
Severity: Will break
What changed: MTREE vector search index was deprecated in 2.x and has been removed.
Action: Use HNSW instead of MTREE in index definitions.
Before (2.x):
DEFINE INDEX vec_idx ON table FIELDS embedding MTREE DIMENSION 768;
After (3.x):
DEFINE INDEX vec_idx ON table FIELDS embedding HNSW DIMENSION 768;
10. Stored closures
Severity: Will break
What changed: Closures can no longer be stored as part of a record.
Action: Use of closures stored inside a record will have to be removed, there is currently no new feature which can replace the stored closures.
Before (2.x):
CREATE record SET closure = |$a| $a + 1
After (3.x):
CREATE record SET closure = |$a| $a + 1
11. Usage of record references
Severity: Will break
What changed: Record references were an experimental feature in 2.x and in 3.x the syntax of record references has been significantly altered.
Action: Record references in 2.x will have to be updated manually to 3.x syntax.
12. Usage of ANALYZE statement
Severity: Will break
What changed: The ANALYZE statement which could provide some statistics about full text indexes has been removed.
Action: Use the ANALYZE stastement will have to be removed.
Can break - likely issues
13. All .* idiom behavior
Severity: Can break
What changed: The .* (all idiom) behavior changed for arrays and objects.
Breaks when: Used to dereference record IDs in arrays or get object values.
Before (2.x):
[a:1, a:2].*
[a:1, a:2].*.*
{ a: 1, b: "foo" }.*
After (3.x):
[a:1, a:2].*
{ a: 1, b: "foo" }.*
Migration:
- For arrays: Replace
.*.* with .* - For objects: Replace
.* with object::values() function
14. Field idiom followed by another idiom part
Severity: Can break
What changed: Field idioms on arrays now work on individual elements instead of the whole array.
Breaks when: Field idiom on array of objects is followed by another idiom part.
Before (2.x):
[{ a: ["a","b"]}, {a: [1,2]}].a[0]
After (3.x):
[{ a: ["a","b"]}, {a: [1,2]}].a[0]
Migration: Swap idiom parts if old behavior needed.
- Old:
.field[0] - New:
[0].field
15. Idiom fetching changes
Severity: Can break
What changed: Multiple improvements to idiom fetching behavior.
Quick Reference Table:
| Example | 2.x Output | 3.x Output |
|---|
[1, a:1].* | [1, a:1] | [1, { id: a:1 }] |
[1, a:1].*.* | [NONE, { id: a:1 }] | [NONE, { id: a:1 }] |
a:1.* | { id: a:1 } | { id: a:1 } |
{ key: 123 }.* | [123] | { key: 123 } |
a:1<-edge[0] | { id: edge:1 } | edge:1 |
[{ n: 1 }, { n: 2 }].n[0] | 1 | [NONE, NONE] |
Action: Review queries using these idioms and rewrite if necessary.
16. Optional parts syntax change
Severity: Can break
What changed: Optional operator changed from ? to .?
Action: Replace ? with .? after optional values.
Before (2.x):
["string", NONE].map(|$val| $val?.len());
After (3.x):
["string", NONE].map(|$val| $val.?.len());
Reason: Distinguishes between ?? operator and optional chaining on option<option<value>>.
17. Parsing changes
Severity: Can break
Record ID parsing:
r"a:b[r"c:d"]"
r"a:b[r\"c:d\"]"
Unicode parsing:
"\uD83D\uDF15"
"\u{1F715}"
Identifier escaping: Escaped identifiers now support escape sequences like \n, \u{AB1234}.
18. New set type behaviour
Severity: Can break
What changed: Set type now both deduplicates AND orders items, displays with {} instead of [].
Before (2.x):
<set>[2,3,1,1];
After (3.x):
<set>[2,3,1,1];
Migration Options:
- Use new set type (recommended)
- Maintain old behavior: Define as
array adding VALUE $value.distinct() to DEFINE FIELD definition
19. Schema strictness changes
Severity: Can break
Non-existing tables:
SELECT * FROM doesnt_exist;
SCHEMAFULL Tables:
DEFINE TABLE user SCHEMAFULL;
DEFINE FIELD name ON user TYPE string;
CREATE user CONTENT { name: "Billy", other: "value" };
CREATE user CONTENT { name: "Billy", other: "value" }.{ name };
20. Numeric record ID ordering
Severity: Can break
What changed: Numeric values in record now have different ordering and equality when used in keys. Previously, a:[1], a:[1f] and a:[1dec] were all different record IDs and could have different records.
Numeric values in record IDs are now ordered by their numeric value, meaning the a:[1], a:[1f] and a:[1dec] are the same key. Furthermore, a:[0f] is now ordered before a:[1].
Breaks when: Code depends on different numeric types resulting in different record IDs.
Before (2.x):
CREATE t:[1];
CREATE t:[1f];
SELECT * FROM t;
After (3.x):
CREATE t:[1];
CREATE t:[1f];
SELECT * FROM t;
Unlikely break - edge cases
21. math::sqrt returns NaN
Severity: Unlikely break
What changed: Returns NaN instead of NONE for negative numbers.
Action: Change checks from NONE to NaN.
math::sqrt(-1);
math::sqrt(-1);
22. math::min returns Infinity
Severity: Unlikely break
What changed: Returns Infinity instead of NONE for empty arrays.
Action: Change checks from NONE to Infinity.
math::min([]);
math::min([]);
23. math::max returns -Infinity
Severity: Unlikely break
What changed: Returns -Infinity instead of NONE for empty arrays.
Action: Change checks from NONE to -Infinity.
math::max([]);
math::max([]);
24. array::logical_and Behavior
Severity: Unlikely break
What changed: Function is now consistent with && operator.
Breaks when: Relying on specific values rather than truthiness.
Before (2.x):
array::logical_and(["a"],[true]);
array::logical_and([""],[false]);
array::logical_and([true],[]);
After (3.x):
array::logical_and(["a"],[true]);
array::logical_and([""],[false]);
array::logical_and([true],[]);
Action: Update if relying on specific return values; no change needed if only checking truthiness.
25. array::logical_or behavior
Severity: Unlikely break
What changed: Function now consistent with || operator.
Breaks when: Relying on specific values rather than truthiness.
Before (2.x):
array::logical_or(["a"],[true]);
array::logical_or([""],[false]);
array::logical_or([],[false]);
After (3.x):
array::logical_or(["a"],[true]);
array::logical_or([""],[false]);
array::logical_or([false],[]);
Action: Update if relying on specific return values; no change needed if only checking truthiness.
26. Mock value type changes
Severity: Unlikely break
What changed: Mocks now return arrays instead of special mock type.
Breaks when: Code depends on the specific mock type being returned.
Before (2.x):
|a:1..2|;
type::is_array(|a:1..2|);
After (3.x):
|a:1..=2|;
type::is_array(|a:1..=2|);
Mock ranges are no longer inclusive by default - use ..= for inclusive ranges.
27. Id field special behavior.
Severity: Unlikely break
What changed: Special behavior regarding .id idioms is removed.
Before 3.0, .id idioms followed by another idiom expression would return the record-id key. After 3.0, the .id behaves like any other .field idiom.
Breaks when: Code depends the special behavior of that .id idioms had.
Before (2.x):
record:{ key_field: "value" }.id.key_field
After (3.x):
record:{ key_field: "value" }.id.key_field
record:{ key_field: "value" }.id().key_field
28. Expressions now allowed inside queries
Many statements had parts changed to support general expressions in those places. This means that identifiers which overlap with statements are no longer supported in those places without escaping. For example, syntax like the following was previously allowed:
DEFINE INDEX select ...
This must now be written with backticks, or renamed.
DEFINE INDEX `select` ...
The statements which had this change from an identifier to allowing a general expressions are the following:
- The
ident after DEFINE TABLE ident ... - The
ident after DEFINE NAMESPACE ident ... - The
ident after DEFINE DATABASE ident ... - The
ident after DEFINE USER ident ... - The
ident after DEFINE ACCESS ident ... - Both
ident and table after DEFINE EVENT ident ON table ... - Both
ident and table after DEFINE FIELD ident ON table ... - The
ident after DEFINE ANALYZER ident ... - The
ident after DEFINE BUCKET ident ... - The
ident after DEFINE SEQUENCE ident ... - The
ident after INFO FOR TABLE ident ... - The
ident after INFO FOR USER ident ... - Both
ident and table after INFO FOR INDEX ident ON table ... - The
ident after REMOVE TABLE ident ... - The
ident after REMOVE NAMESPACE ident ... - The
ident after REMOVE DATABASE ident ... - The
ident after REMOVE USER ident ... - The
ident after REMOVE ACCESS ident ... - Both
ident and table after REMOVE EVENT ident ON table ... - Both
ident and table after REMOVE FIELD ident ON table ... - Both
ident and table after REMOVE INDEX ident ON table ... - The
ident after REMOVE ANALYZER ident ... - The
ident after REMOVE BUCKET ident ... - The
ident after REMOVE SEQUENCE ident ...
29. DEFINE FIELD number of items for arrays and sets
A DEFINE FIELD statement for arrays and sets in SurrealDB 2.x allowed a maximum number of items to be indicated. This number now refers to the required number of items.
As such, a schema with an ASSERT $value().len() is equal to a certain number can now have the required number in the type definition itself. Additionally, definitions that indicate a maximum number of items must be changed to ASSERT $value.len() <= followed by the maximum number.
DEFINE FIELD bytes ON data TYPE array<int> ASSERT $value.all(|$val| $val IN 0..=255) AND $value.len() = 640;
DEFINE FIELD bytes ON data TYPE array<int, 640> ASSERT $value.all(|$val| $val IN 0..=255);
DEFINE FIELD latest ON observation TYPE array<object> ASSERT $value.len() <= 1000;